Barnyard Millet: Benefits, Nutrition, Uses, Recipes & More

Barnyard Millet Benefits: In the pursuit of holistic wellness and optimal nutrition, ancient grains are experiencing a significant resurgence. Among these, barnyard millet (Echinochloa esculenta and Echinochloa frumentacea) stands out as a remarkably nutritious and versatile grain, often referred to by various regional names such as Sanwa rice, Sama ke chawal, Kuthiraivali, and Oodalu.
This hardy cereal, belonging to the Poaceae grass family, has been a dietary staple for centuries in many parts of Asia. Its resilience, rapid growth, and exceptional nutritional profile make it an increasingly relevant food choice in today's health-conscious world. As we navigate the complexities of modern diets, understanding the profound Barnyard millet benefits and its rich Nutritional Profile is key to unlocking its potential for transforming our health. This article delves into the multifaceted advantages of barnyard millet, from managing chronic conditions to enhancing daily well-being, and explores its diverse culinary applications.
What Is Barnyard Millet?
Barnyard millet, scientifically known as Echinochloa esculenta or Echinochloa frumentacea, is a drought-tolerant and fast-growing annual grass belonging to the Poaceae family. It is one of the oldest cultivated grains, with a history stretching back thousands of years, particularly in regions of Asia like India and China.
Commonly known by names such as Sanwa rice, Sama ke chawal (in Hindi), Kuthiraivali (in Tamil), and Oodalu (in Kannada), this gluten-free grain is gaining widespread recognition for its impressive health attributes. Its small, pearl-like seeds can be prepared in various ways, often serving as a wholesome substitute for more refined grains. The grain's adaptability to diverse weather conditions and its ability to germinate effectively contribute to its historical significance and renewed popularity.
Beyond its grain form, innovative preparations like Sprout Activated Barnyard Millet highlight the potential of its germination process to further enhance nutrient availability. Its cultivation is a testament to agricultural wisdom, often thriving in conditions where other crops might falter, making it a sustainable and resilient food source.
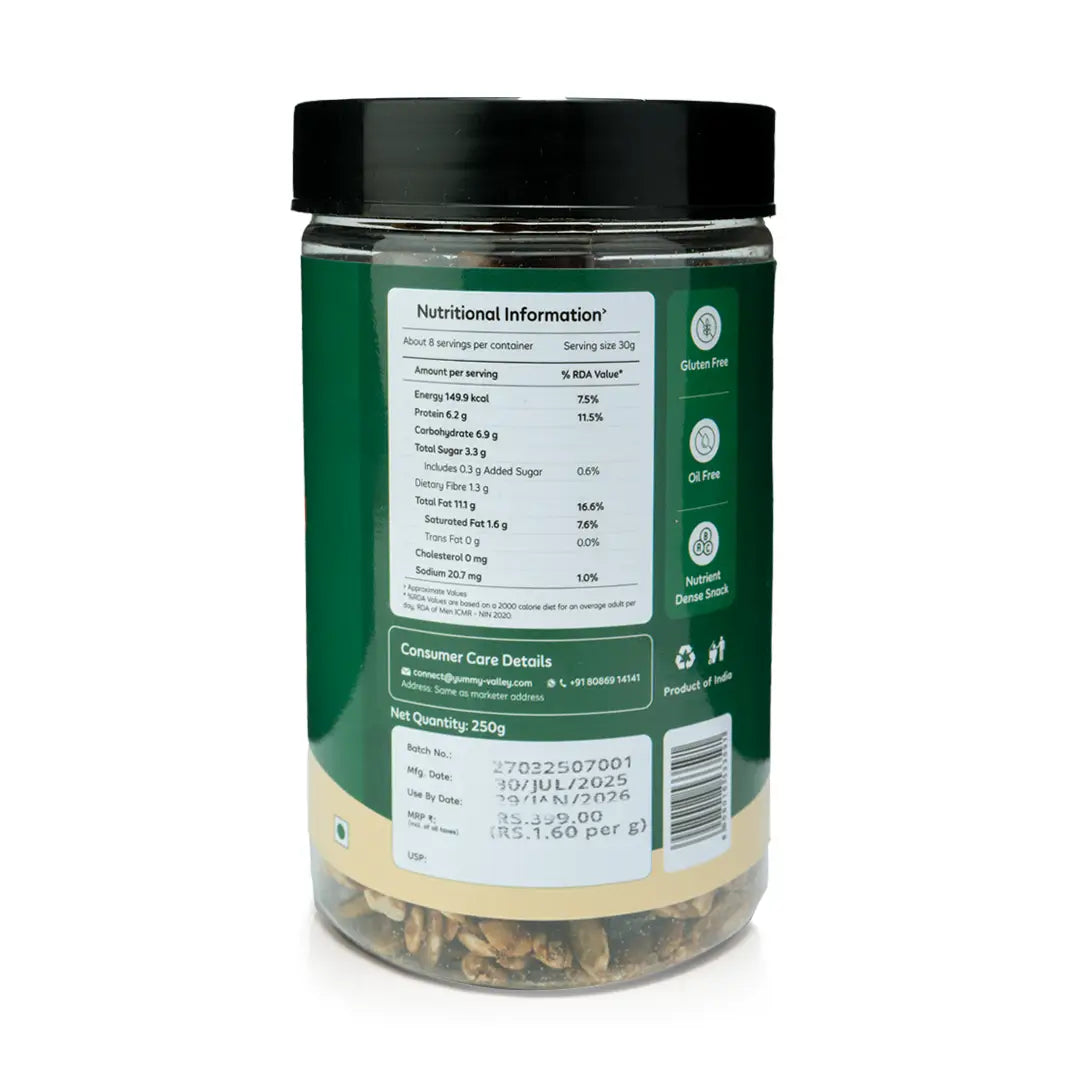
Barnyard Millet Nutritional Value per 100g
Curious about Barnyard millet’s nutritional benefits? It’s loaded with dietary fibre, iron, phosphorus, and antioxidants. What’s more, its phenol content grants it antibacterial, anti-ageing, and antibiotic properties. According to the Phyto journal, here’s the barnyard millet nutritional value per 100g:
| Nutrients | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Protein | 10.5 |
| Fat | 3.6 |
| Crude Fibre | 6.6 |
| Total minerals | 2.0 |
| Total Carbohydrates | 68.8 |
| Calorific value | 398.0 |
| Total dietary fibre | 12.6 |
| Soluble dietary fibre | 4.2 |
| Insoluble dietary fibre | 8.4 |
| Phosphorus | 281 mg |
| Iron | 5 mg |
| Magnesium | 83 mg |
| Calcium | 19 mg |
Barnyard millet’s advantages aren’t just limited to a couple of health benefits; they contribute to various metabolic functions by lowering bad cholesterol and boosting good cholesterol. This supports heart health and aids in weight management.
Health Benefits Of Barnyard Millet
1. Manage type 2 diabetes
Barnyard millet is a highly recommended food for individuals managing type II diabetes due to its exceptionally low glycemic index (GI). Foods with a low GI are absorbed slowly, leading to a gradual rise in blood sugar levels rather than sharp spikes. Research from NCBI indicates that processed barnyard millet can significantly help manage type II diabetes.
Its rich polyphenol content actively inhibits the breakdown of complex sugars into glucose, thereby improving glucose control. This makes barnyard millet an excellent choice for a diabetic-friendly diet, helping to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing diabetes-related complications. Studies have also shown that dehulled and heat-treated barnyard millet possesses properties that can help manage type II diabetes more effectively.
2. Maintains heart health
The incorporation of barnyard millet into one's diet can significantly contribute to maintaining excellent heart health. Its nutrient-dense composition reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases. resistant starches, which can be particularly beneficial for patients with cardiovascular diseases. High magnesium content in barnyard millet is known to aid in reducing blood pressure.
Furthermore, the significant magnesium content in barnyard millet is known to aid in blood pressure reduction. The high magnesium content of barnyard millet is known to help reduce. The high dietary fibre content actively lowers LDL ("bad") cholesterol while promoting increases in HDL ("good") cholesterol, a crucial factor in preventing heart disease.
3. Fights against anaemia
Barnyard millet's impressive iron content makes it a potent ally in the fight against anaemia. Anaemia, often characterised by chronic fatigue and low energy levels, stems from an iron deficiency, which is essential for the production of red blood cells and the efficient transport of oxygen throughout the body.
Consuming controlled portions of this nutrient-rich grain provides the vital iron and other nutrients necessary for a healthy metabolism. For individuals experiencing constant fatigue and energy depletion due to anaemia, integrating barnyard millet into their diet can effectively alleviate these symptoms and help restore vitality.
4. Skin and hair benefits
The health benefits of barnyard millet extend to enhancing the vitality and appearance of skin and hair. Its rich concentration of phenols and flavonoids makes it an exceptional source of antioxidants. These compounds play a crucial role in combating oxidative stress, neutralising free radicals, and protecting skin cells from damage, thereby contributing to a more youthful and radiant complexion.
Additionally, iron in barnyard millet is vital for healthy hair follicles, promoting robust hair growth and preventing premature hair loss. The zinc content further supports scalp health and hair strength.
5. Manages digestive disorders
Barnyard millet is a true boon for individuals struggling with various gastrointestinal issues, effectively easing a range of digestive problems. The substantial dietary fibre content promotes regular, smooth bowel movements, thereby helping ward off common ailments such as constipation, acidity, bloating, and painful stomach cramps.
Regular consumption can also help reduce the risk of more serious conditions like colon cancer, haemorrhoids, and diverticular disease. By nourishing beneficial gut bacteria and improving the overall gut microbiome, barnyard millet plays a significant role in enhancing digestive health and bolstering the body's immunity.
Also Read: Finger Millet Benefits & Side Effects
Uses Of Barnyard Millet
The versatility of barnyard millet makes it a valuable ingredient across a spectrum of culinary applications, offering a nutritious and delicious alternative to conventional grains. Its small, round grains can be prepared in numerous ways, making them suitable for both savoury and sweet dishes.
- Rice: One of the most straightforward uses is as a rice substitute. Barnyard millet can be cooked with water or vegetable broth and served alongside curries, dals, sambars, or any other gravies. It offers a texture and flavour profile akin to broken rice but with significantly greater health benefits.
- Porridge: For a comforting and wholesome meal, barnyard millet can be transformed into a flavourful porridge. This can be prepared either sweet or savoury, using milk or water as the base. To enhance its taste and nutritional value, one can add sweeteners such as sugar, honey, or jaggery, as well as spices like cardamom, cinnamon, or nutmeg. Fruits, nuts, and seeds can further enrich the porridge.
- Upma: A popular Indian breakfast dish, Upma, can be made exceptionally healthy with barnyard millet. Typically prepared with mustard seeds, curry leaves, asafoetida, onions, and green chillies, it becomes a filling and nutrient-dense meal. The barnyard millet upma offers a satisfying alternative to semolina-based upma.
- Dosa: Beyond these common preparations, barnyard millet can be ground into Barnyard millet flour, gluten-free diet, like rotis, pancakes, and breads. It is also used to create Barnyard Millet Vermicelli, offering a novel pasta alternative. Its adaptability ensures that Barnyard millet recipes can cater to diverse tastes and dietary needs, promoting overall well-being through delicious food.
Barnyard Millet Recipes for Better Health
Incorporating barnyard millet into your daily meals is a straightforward yet impactful way to boost your health and well-being. Whether you are seeking weight loss solutions or simply aiming for a more nutrient-dense diet, these Barnyard millet recipes offer delicious and easy ways to harness its extensive health benefits. Designed for simplicity and speed, these dishes are comforting, nourishing, and rich in nutrients, making healthy eating an enjoyable experience.
1. Barnyard Millet Dosa Recipe

Barnyard millet dosa provides a delightful crunch and is an incredibly nutritious breakfast option, simple to prepare and utterly satisfying. This gluten-free and diabetic-friendly dietary fibre, protein, iron, and calcium. Its consumption is linked to potential benefits, including blood sugar regulation, cholesterol management, blood pressure control, improved digestive health, and boosted immunity. Embracing this millet dosa is an excellent step towards integrating this nutritious grain into your diet and relishing its advantages.
Ingredients
- 1 cup barnyard millet
- 1/4 cup urad dal
- 1/4 cup poha
- 1 teaspoon methi seeds
- Salt to taste
- Oil or ghee for frying
- Water as needed
Instructions
- Soaking: Wash and soak the barnyard millet, urad dal, poha, and methi seeds separately in bowls for at least 4 hours.
- Grinding Millet: Drain the water from the soaked millet and grind it coarsely in a mixer or grinder. Transfer this coarse mixture to a large mixing bowl.
- Grinding Dal Mixture: In the same mixer or grinder, grind the soaked urad dal, poha, and methi seeds to a smooth paste. Add water gradually to achieve a smooth, flowing consistency. Transfer this paste to the same bowl containing the millet.
- Fermentation: Thoroughly blend the two batters together. Season with salt according to your preference. Cover the bowl and allow it to ferment in a warm place for 8-12 hours or overnight.
- Cooking Dosa: Heat a dosa tawa or griddle over medium-high heat. Lightly grease it with oil or ghee. Ladle a portion of the fermented batter onto the hot tawa and spread it outwards in a circular motion to form a thin, even dosa. Drizzle a little oil or ghee around the edges and cook until the dosa turns golden brown and crispy.
Recipe Notes
- Flavour Boost: For enhanced taste, you can incorporate finely chopped green chillies, grated ginger, fresh curry leaves, or cumin seeds into the batter before fermentation.
- Storage: Leftover batter can be stored in an airtight container in the refrigerator for up to three days. You may need to add a splash of water to achieve the correct consistency before cooking.
- Idli Variation: The same batter can be used to make idlis. Steam them in idli moulds for 10-15 minutes.
2. Barnyard Millet Upma Recipe

Barnyard millet upma is a highly nourishing and satisfying meal, perfect for breakfast or lunch. Known locally as Kuthiraivali in Malayalam, this grain is a gluten-free wonder with a low glycemic index. It is densely packed with dietary fibre, protein, iron, and calcium, offering potential benefits for managing blood sugar levels, cholesterol, and blood pressure, while also promoting improved digestive health and immunity.
This barnyard millet upma is a simple and quick recipe, requiring minimal ingredients and spices. You can also elevate its nutritional profile and visual appeal by adding your favourite chopped vegetables.
Ingredients
- 1 cup barnyard millet
- 2 cups water
- 1 tbsp oil
- 1 tsp mustard seeds
- 1 tsp urad dal
- A pinch of asafoetida
- A few curry leaves
- 1 onion, finely chopped
- 2 green chillies, slit
- 1 tsp ginger-garlic paste
- 1/4 tsp turmeric powder
- Salt to taste
- 1/4 cup chopped coriander leaves
Instructions
- Prepare Millet: Wash the barnyard millet thoroughly and soak it in water for about 30 minutes. Drain the water and set the millet aside.
- Temper Spices: Heat oil in a pressure cooker or a heavy-bottomed pan. Add the mustard seeds, urad dal, asafoetida, and curry leaves. Allow the mustard seeds to splutter.
- Sauté Aromatics: Add the finely chopped onion, slit green chillies, and ginger-garlic paste. Sauté until the onions turn golden brown and are well softened.
- Add Spices and Millet: Stir in the turmeric powder and salt. Mix well. Add the soaked barnyard millet and 2 cups of water. Stir everything together.
- Cook: Close the lid of the pressure cooker. Cook for 3 whistles on high heat, then reduce the flame and cook for another 5 minutes. If using a pan, cover and simmer until the millet is cooked and the water is absorbed.
- Finish and Garnish: Once cooked, turn off the flame and allow the pressure to release naturally. Open the lid, gently fluff the upma with a fork, and garnish generously with chopped coriander leaves.
- Serve: Serve the hot barnyard millet upma with coconut chutney, sambar, or your favourite pickle.
Recipe Notes
- Vegetable Inclusion: Feel free to add finely chopped vegetables like carrots, peas, beans, or capsicum along with the onion for a more nutritious and colourful dish.
- Ghee Enhancement: For a richer taste and aroma, consider using ghee instead of oil for tempering.
- Consistency Adjustment: The water quantity may need slight adjustment based on the specific type of barnyard millet and your preferred consistency. Barnyard millet typically requires a bit more water than rice.
3. Barnyard Millet Fried Rice Recipe

Barnyard millet transforms into an exceptionally delicious and wholesome fried rice, offering a fantastic, healthy alternative to traditional rice-based dishes. This recipe showcases the grain's ability to absorb flavours beautifully, making for a vibrant and satisfying meal. Barnyard millet recipes provide a nutritious, gluten-free, and low carbohydrate. Let's cook up some delectable barnyard millet fried rice!
Ingredients
- 1 cup barnyard millet, soaked for 30 minutes and drained
- 2 cups water
- Salt to taste
- 2 tablespoons oil
- 1 teaspoon cumin seeds
- 1 onion, finely chopped
- 2 green chillies, slit
- 1/4 teaspoon turmeric powder
- 1/4 teaspoon red chilli powder
- 1/4 teaspoon garam masala
- 2 cups mixed vegetables, chopped (carrots, beans, peas, corn, etc.)
- 2 tablespoons coriander leaves, chopped
- Lemon juice to taste
Instructions
- Cook Barnyard Millet: In a pressure cooker, combine the soaked barnyard millet, 2 cups of water, and a pinch of salt. Cook for 3 whistles or until the millet is soft and fluffy. Alternatively, cook in a pot until tender. Once cooked, fluff the millet gently with a fork and set aside.
- Sauté Aromatics: Heat the oil in a large wok or pan over medium-high heat. Add the cumin seeds and let them splutter. Then, add the chopped onion and slit green chillies. Sauté until the onions turn translucent and slightly golden.
- Add Spices: Stir in the turmeric powder, red chilli powder, garam masala, and a pinch more salt. Sauté for about a minute until the spices are fragrant.
- Stir-fry Vegetables: Add the mixed chopped vegetables to the pan. Stir-fry them for approximately 8-10 minutes until they are tender-crisp.
- Combine and Toss: Gently add the cooked barnyard millet to the pan with the vegetables. Mix everything thoroughly, ensuring the millet is evenly coated with the spices and vegetable mixture. Cook for another 2-3 minutes, allowing the flavours to meld.
- Garnish and Serve: Sprinkle the chopped coriander leaves and a squeeze of fresh lemon juice over the fried rice. Toss gently. Serve the barnyard millet fried rice hot, either as a standalone meal or as a side dish.
Recipe Notes
- Protein Boost: Enhance the protein content by adding cubed paneer, tofu, pre-cooked chicken pieces, or scrambled eggs to the vegetable mix.
- Flavour Variations: Experiment with different oils like coconut oil or ghee for a distinct flavour profile.
- Nutty Crunch: For added texture and nutty goodness, toss in some roasted peanuts or cashews along with the vegetables.
Side Effects Of Barnyard Millet
While barnyard millet offers a wealth of health benefits, like any food, excessive consumption or individual sensitivities might lead to certain side effects. It's important to be aware of these potential issues and consume the grain in moderation. The primary considerations revolve around its fibre content, potential goitrogenic compounds, and the presence of phytic acid.
1. Thyroid Function
Similar to other millets, barnyard millet contains naturally occurring compounds called goitrogens. These substances have the potential to interfere with thyroid hormone production, particularly if consumed in very large quantities by individuals with pre-existing thyroid conditions or iodine deficiency.
While research suggests that the levels in barnyard millet are generally considered safe for most people, those with thyroid concerns, such as hypothyroidism, should consult with their healthcare provider before making barnyard millet a staple in their diet. Proper preparation methods, like soaking and cooking, can also help reduce the goitrogenic potential.
2. Digestion
The high dietary fibre content in barnyard millet is a significant contributor to its digestive health benefits, aiding in regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. However, for individuals not accustomed to a high-fiber diet, a sudden increase in fiber intake can sometimes lead to temporary digestive discomfort, including bloating, gas, or abdominal cramping. To mitigate this, it is advisable to gradually introduce barnyard millet into your diet, increase your water intake significantly, and ensure thorough soaking or sprouting of the grain before cooking. These practices help break down complex compounds and make the millet easier to digest.
3. Allergy
Although rare, some individuals may experience an allergic reaction to barnyard millet. Symptoms can range from mild skin rashes, itching, or swelling to more severe reactions like breathing difficulties. If you notice any such signs after consuming barnyard millet, it is crucial to discontinue its intake immediately and seek medical attention. As with any new food, it's wise to start with small quantities to assess your body's tolerance.
4. Nutrient Absorption
Barnyard millet contains phytic acid, a compound found in many grains and legumes. Phytic acid can bind to certain minerals, such as iron, zinc, calcium, and magnesium, potentially hindering their absorption in the digestive tract. This can, over time, impact the bioavailability of these essential minerals. To counteract this effect, several preparation methods can be employed. Soaking, sprouting, or fermenting the barnyard millet before cooking can significantly reduce phytic acid levels, thereby enhancing mineral absorption. Additionally, pairing barnyard millet with foods rich in Vitamin C, like citrus fruits, tomatoes, or bell peppers, can further aid in the absorption of iron and other minerals.
Conclusion
Barnyard millet, with its ancient roots and modern relevance, emerges as a truly exceptional grain that deserves a prominent place in our diets. Its impressive Nutritional Profile, characterised by high dietary fibre, digestible protein, and a wealth of Essential Nutrients, underpins its remarkable array of health benefits. From its significant role in managing blood sugar levels and supporting a diabetic-friendly diet due to its low glycemic index, to its contribution to weight loss and enhanced digestive health, barnyard millet offers a holistic approach to well-being. Its gluten-free nature makes it a safe and valuable option for those with celiac disease and gluten intolerance, while its impact on heart health and protection against cardiovascular diseases further solidifies its position as a superfood.
The versatility of barnyard millet, evident in delicious barnyard millet upma, barnyard millet dosa, and numerous other Barnyard millet recipes, makes it easy and enjoyable to incorporate into daily meals. As awareness grows and its market presence expands, with brands like Organic Mandya, Desinutri Foods, and Bliss Tree offering various forms, including Sprout Activated Barnyard Millet, consumers have more access than ever. By choosing this resilient and nutritious grain, you are not only investing in your personal health but also supporting a sustainable and ancient food system. Embracing barnyard millet is a step towards a healthier, more vibrant you.
FAQs: Barnyard Millet
What nutrients does Barnyard millet contain?
Barnyard millet is exceptionally rich in essential nutrients. It contains a good amount of iron, magnesium, and phosphorus, which are crucial for various bodily functions. Additionally, it is a source of beneficial phenols and flavonoids, acting as potent antioxidants.
The grain is also lauded for its high content of both soluble and insoluble dietary fibres, which are fundamental for promoting digestive health. These nutrients collectively support a range of health conditions, contributing to better blood pressure regulation, cholesterol management, effective weight loss strategies, and the relief of irregular bowel movements.
Does Barnyard millet aid digestion?
Absolutely. The significant presence of both soluble and insoluble dietary fibres in barnyard millet is a key factor in its ability to promote excellent digestive health. These fibres contribute to smoother bowel movements, effectively alleviating constipation and supporting overall gut function.
How does Barnyard millet compare to rice?
Barnyard millet offers a distinct nutritional advantage over polished white rice. While rice is primarily a source of carbohydrates, barnyard millet boasts a much lower glycemic index, making it a superior choice for managing blood sugar levels and supporting a diabetic-friendly diet. It is also packed with a richer array of Essential Nutrients, including iron, magnesium, and various B vitamins, which are often lacking in refined rice. This makes barnyard millet a more nutritionally dense and beneficial alternative.
Is Barnyard millet a good source of protein?
Yes, barnyard millet is indeed a good source of protein. It contains a substantial amount of digestible protein, which is essential for muscle repair, growth, and overall bodily functions. This protein content, combined with other vital nutrients, further enhances its value as a healthy dietary staple.
What are the health perks of barnyard millet?
The health perks of barnyard millet are extensive and varied. It offers abundant dietary fibre, acting as a prebiotic and promoting optimal digestive health. Its antioxidant properties help combat cellular damage. Due to its low glycemic index and fibre content, it is highly beneficial for weight management and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Furthermore, as a gluten-free grain, it serves as an excellent and safe option for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance. Its contribution to heart health by managing cholesterol and blood pressure is also a significant advantage.